The balance sheet will appear as if the stock was neverissued in the first place. However, the accounting for the issuance of common stock doesn’t involve two entries, like most other transactions. It also impacts another financial account, which is the share premium account. As mentioned, this account records any exchange amount received above the par value. The amount in this account will include the difference between the funds received and the par value. 5As mentioned earlier, the issuance of capital stock is not viewed as a trade by the corporation because it merely increases the number of capital shares outstanding.
- This accounting treatment also differentiates this finance source on the balance sheet.
- The difference between issuance price and par value is recorded as Additional Paid-In Capital.
- The following journal entry is recorded forthe purchase of the treasury stock under the cost method.
- They will be entitled to receive company assets in the event of liquidation after all creditors are settled.
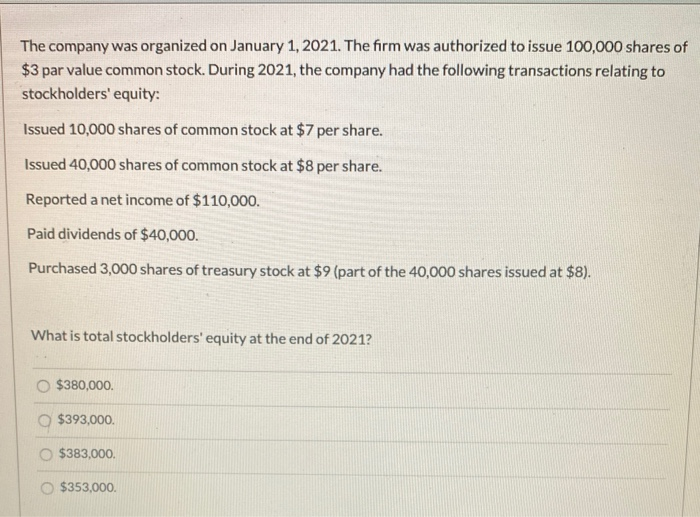
1: The Issuance of Common Stock
It is printed on the face of an old fashioned stock certificate and indicates (again depending on state law) the minimum amount of money that owners must legally leave in the business. Shares authorized is the number of shares a corporation is allowed to issue (sell). For a large corporation, this is based on a decision by its Board of Directors, a group elected to represent and serve the interest of the stockholders.
Navigating the Disadvantages of Purchasing Processes (3 Points You Should Know
Common stock has also been mentioned in connection with the capital contributed to a company by its owners. We have a debit to the fixed assets account, with an increase of $1,500,000. We then have two credit entries, the first being $100,000 to theClass A Share Capital, which records the par value of the shares exchanged. And then the $1,400,000, which records the addition paid-in capital, or the share premium Kevin paid.
Journal entry for issuing common stock for non-cash asset
In either case, both total assets and total equity will increase in the issuance of the common stock journal entry. Common shares represent ownership in a company, and holders of common shares are entitled to a share of the company’s profits and assets. When a company issues common shares, it is effectively selling ownership stakes in the company to the investors who purchase the shares. In this journal entry, the total expenses on the income statement and the total equity on the balance sheet increase by the same amount. The expense amount in this journal entry is the fair value of the service that the corporation receives in exchange for giving up the shares of the common stock.
3 Accounting for the issuance of common stock
Once the Board approves the transaction and the paperwork is complete, the ABC accounts team would prepare the following journal entry. The last example we will look at in the journal entry for the issue of common stock is company share buy-backs. The issuance of common stock for a non-cash exchange is less common than for cash, but you will often see this either say in a merger or acquisition or closely held companies. In an acquisition situation, we will often see the exchange of shares for shares. For example, company A will acquire company B, giving company B shareholders a mix of company A shares and cash. For example, the company ABC issues the above shares of common stock for $100,000 which is at the price of $5 per share instead of $1 per share.
Reporting Treasury Stock for Nestlé Holdings Group

Issuing common stock in exchange for a capital contribution has the advantage that unlike a loan, the business doesn’t have to pay back an equity investment. However, the investor who buys the stock has an ownership interest in the company, and the company has to make proper accounting entries in order to reflect the new capital contribution. The accounting for the issuance of a common stock involves several steps. However, it is crucial to understand that every share has a par value. This par value represents the share’s value in the company’s articles.
The common stockholders are the owner of the company and they have the right to vote for the company director, board, and request for change in the management team. It means the stockholder has the right to control and change the company structure and policy. Special cases For most publicly traded companies, stock offerings are made for cash. But small businesses often have more flexible arrangements to raise capital. And as we know before, 5 per cent of this is the par value, and the remaining 95 per cent is the additional paid-in capital or premium the shareholders are paying above par value. In the case of an oversubscription, the prospectus stated that the share bundles would be allocated on a first-come-first-serve basis.
Unless the stock market value is not available, then asset fair value will be use. Par Value or Face Value or nominal value is the value state on the share or bond. Common Share par value is the legal value state in the company article of memorandum. Total stock par value is the amount that protects the corporate creditor in the case of liquidation. The shareholders are not allowed to withdraw the total capital from the company.
That is different from, for example, giving up an asset such as a truck in exchange for a computer or some other type of property. There are three types of transactions you will need to know when preparing a journal entry for common stock. These are issuing stock exchange for cash, for other non-cash assets how to estimate bad debt expense or companies buying back their own stock. This journal entry for issuing the common stock for the $100,000 cash will increase the total assets and total equity on the balance sheet by the same amount of $100,000 as of January 1. The no-par value stock refers to the common stock that has no par value.
The only difference is the replacement of cash with non-cash assets. The terms above may be better understood with an analogy to a credit card. If you are approved for a credit card, the terms will include a credit limit, such as $5,000, which is the maximum you are allowed to charge on the card.




